What is Greek Mythology and when did it begin?
Greek Mythology is a series of epic tales of bravery, battles, monsters and love told by Ancient Greeks to their families over many generations to help them understand the world around them

READING LEVEL: GREEN
Greek Mythology is a group of epic* stories about Gods, Goddesses, heroes, creatures and the rituals* of Ancient Greece.
Most of these stories were told by the Ancient Greeks to their families and friends over many generations. The stories often featured wars and heroic battles, frightening monsters, and also taught the importance of bravery, intelligence, fear, love, fun and right and wrong.
Many myths were based on the fact that Gods, like human men and women, could be punished or rewarded for their actions.
The Ancient Greeks used myths about Gods to help them understand things happening around them such as the forces of nature. There were sea gods, woodland gods, sky gods, underwater gods, half-gods and human heroes undertaking courageous or romantic adventures.
WHEN DID GREEK MYTHOLOGY BEGIN?
It is difficult to say exactly when Greek Mythology started. Details of the ancient tales have been found on everything from pottery to temples and stone statues over the years.
However, it is believed the first Ancient Greek civilisations* were formed nearly 4000 years ago (approximately 1600 BC) by the Mycenaeans of Crete (a Greek island). The Ancient Greek Empire spread from Greece throughout Europe and, in 800 BC, the Greeks started to split their land into city-states, each with its own laws, customs and rulers.
The largest were Athens, Sparta, Thebes and Corinth.
Each state controlled the territory around a single city, and they were often at war with each other.
Athens became the most powerful city-state and in 508 BC, a new system of rule called democracy* was created by the people. But during that time, only men were allowed to vote.

FIRST WRITTEN TEXT ABOUT GREEK MYTHOLOGY
Around 700 BC, the poet Hesiod’s Theogony offered the first written version of Greek Mythology. Theogony tells the story of the universe’s journey from nothingness (Chaos) to reality, and details a family tree of elements, Gods and Goddesses who evolved from Chaos and descended from:
- Gaia (Earth)
- Ouranos (Sky)
- Pontos (Sea), and
- Tartaros (the Underworld)
The two oldest surviving examples of Greek literature are The Iliad and The Odyssey, epic poems written by Homer that describe the Trojan War, a conflict between the Greeks and the city of Troy fought almost 1200 years before the Common Era.
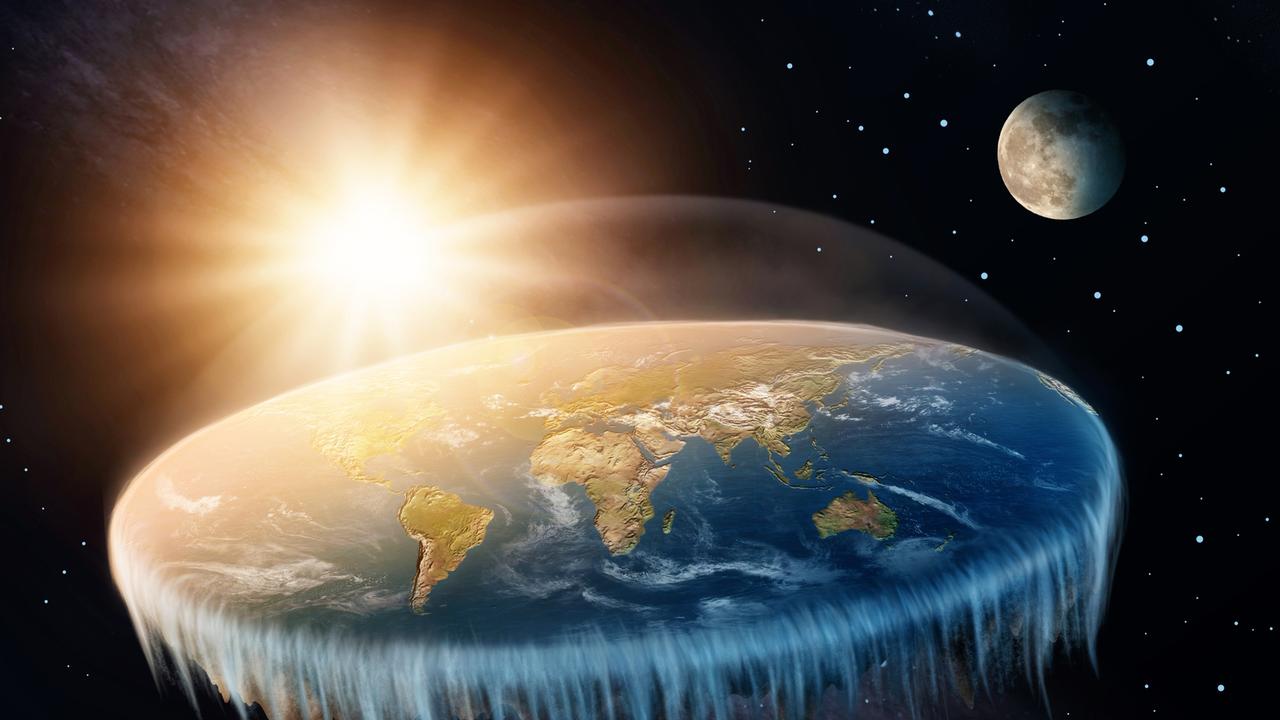

ANCIENT GREEK VIEW OF THE WORLD
The Greeks believed the world was flat, like a plate, and that the centre of the universe was Greece.
Their world was divided by the Mediterranean Sea, which means “Middle of the Lands” in Latin. They believed the river Ocean flowed around the world in a clockwise motion.
In the north lived the Hyperboreans — an extremely happy people for whom life was always rosy. When the old people became tired of living, they simply threw themselves into the sea.
This was a land of endless relaxation where people were said to live for 1000 years.
In the south lived the Ethiopians. In Greek drama, mention is often made of various gods being in Ethiopia, meaning really far away. Ethiopians were said to have good relationships with the Gods and liked to entertain them.
To the west were the Elysian Fields. This was the closest the Greeks got to the idea of heaven — only the best and brightest of the dead were allowed to go there.
VIDEO: Some modern people still believe the Earth is flat.
Ancient Greeks dressed differently, too.
Most wore a chiton, which was similar to a long T-shirt made from one large piece of cotton. The poor slaves, however, had to make do with a loincloth (a small strip of cloth wrapped around the waist).
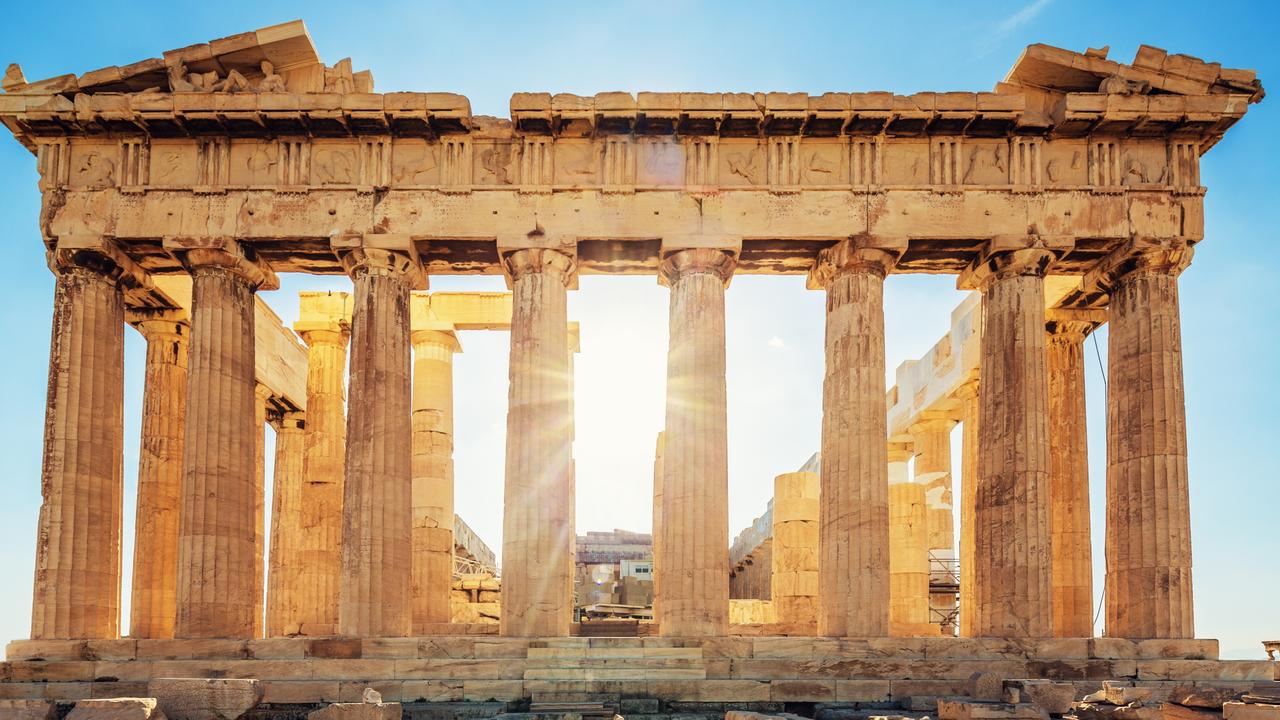

CELEBRATING THE GODS
The Ancient Greeks believed that happy Gods meant happy lives, so they spent a lot of time celebrating the Gods and praying to them.
To show the Gods how important they were, the Greeks built temples in every town for one God or Goddess.
The most famous temple is the Parthenon in Athens. This temple was built for the Goddess Athena, the protector of the city.
The temples were not like modern places of worship, for ordinary people to pray in. They were homes for statues of Gods, which were cared for by priests.
Religious ceremonies and festivals went on outside the temple. To celebrate the God Zeus, for example, the first Greek Olympics were held in the city of Olympia in 776 BC and are thought to have inspired our own Olympic Games.
Rich cities, like Athens, built temples with the best stone, and decorated them with paintings, statues and carvings.

People also had special places in their homes where they could pray to the Gods. There were public shrines in all sorts of places where people could pray and leave presents so the Gods would grant their wishes for things such as a good harvest, a safe journey or for their children to become beautiful.
Priests were important people in the community. They were believed to have the power to talk to the Gods and so were respected and trusted.
There were only two ways you could become a priest. Either your mother or father was a priest or you were made a priest by a dying priest.
A priest’s main job was to look after the temples and the visitors to the temples.
GLOSSARY
- epic: grand or amazing
- rituals: actions performed in a specific order
- civilisations: society, culture, and way of life of a particular area.
- democracy: a system of government elected by the people
EXTRA READING
Part two: The Gods of Mt Olympus
Part three: Greek Gods and their stories
QUICK QUIZ
- How many years ago were the first Ancient Greek civilisations?
- Name the four family tree elements that Gods and Goddesses descended from.
- What were the Elysian Fields?
- How did the Ancient Greeks show the Gods how important they were?
- Who had the power to talk to the Gods?
LISTEN TO THIS STORY
CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES
Refer to the accompanying Greek Myths and Legends classroom workbook with 25 activities. Can be purchased for $5 including GST at https://kidsnews.myshopify.com/products/greek-myths-and-legends.
HAVE YOUR SAY: Do you believe the Earth is round or flat? Why do you believe this?
No one-word answers. Use full sentences to explain your thinking. No comments will show until approved by editors.

