‘Most violent place’ in universe eats the equivalent of a sun a day
Shining 500 trillion times brighter than our sun, a newly identified quasar as old as the origins of the known universe is chomping through the equivalent of 370 suns a year, an Aussie-led team says

READING LEVEL: ORANGE
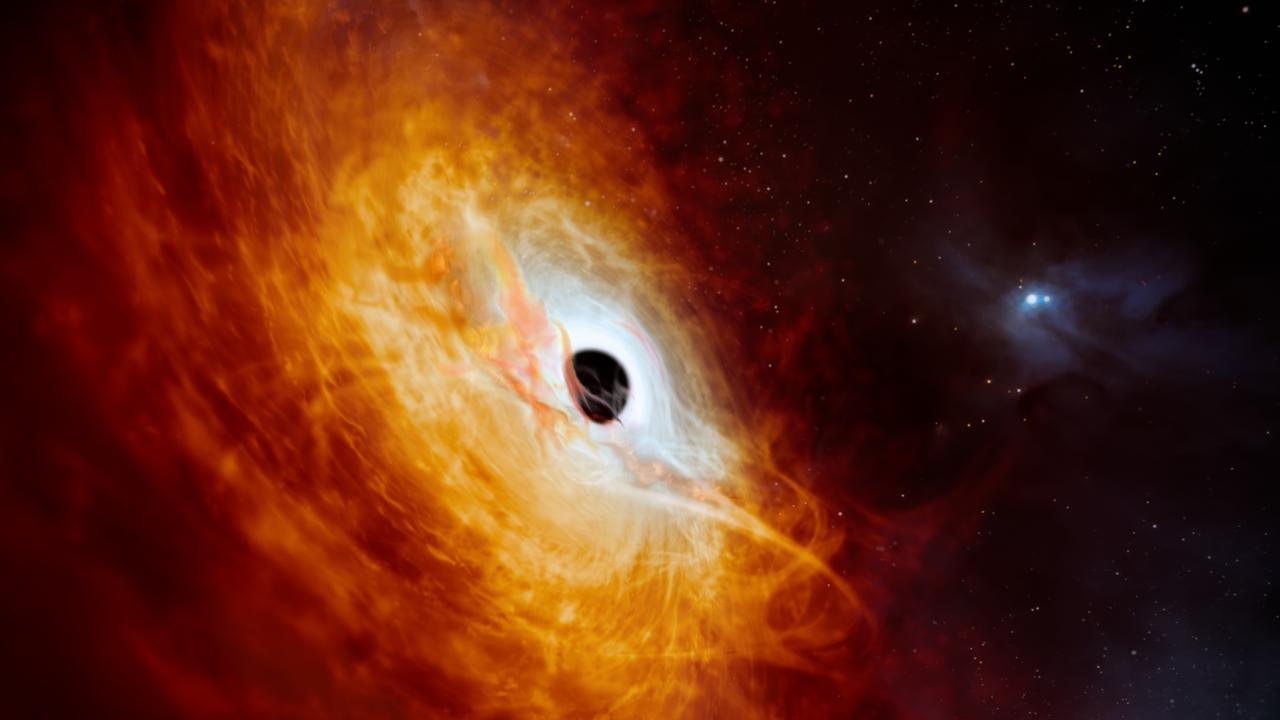
Astronomers* have discovered what may be the brightest object in the universe, a quasar with a black hole at its heart.
Short for “quasi-stellar* radio source”, which means starlike emitter* of radio waves, this particular quasar is growing so fast that it swallows the equivalent* of a sun a day.
The record-breaking quasar shines 500 trillion times brighter than our sun. The black hole powering this distant quasar is more than 17 billion times more immense* than our sun, an Australian-led team reported this week in the journal Nature Astronomy.
While the quasar resembles a mere dot in images, scientists say it is a ferocious* place.
The rotating disc around the quasar’s black hole — the luminous* swirling gas and other matter from gobbled-up stars — is like a cosmic* hurricane.
“This quasar is the most violent place that we know in the universe,” Australian National University Associate Professor and lead author Christian Wolf said in an email.
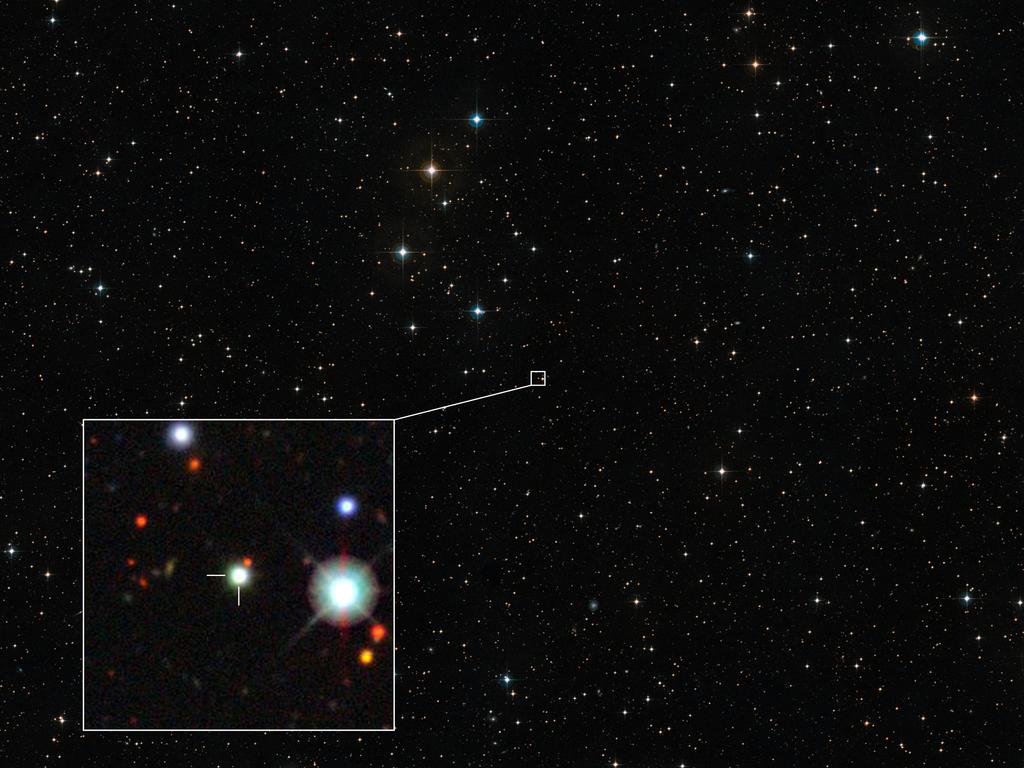
The European Southern Observatory spotted the object, known as J0529-4351, during a 1980 sky survey, but at the time it was thought to be a star. It was not identified as a quasar — the extremely active and luminous core of a galaxy* — until just last year. Observations by telescopes* in Australia and Chile’s Atacama Desert* confirmed it.
“The exciting thing about this quasar is that it was hiding in plain sight and was misclassified* as a star previously,” Yale University Professor Priyamvada Natarajan, who was not involved in the study, said via email.
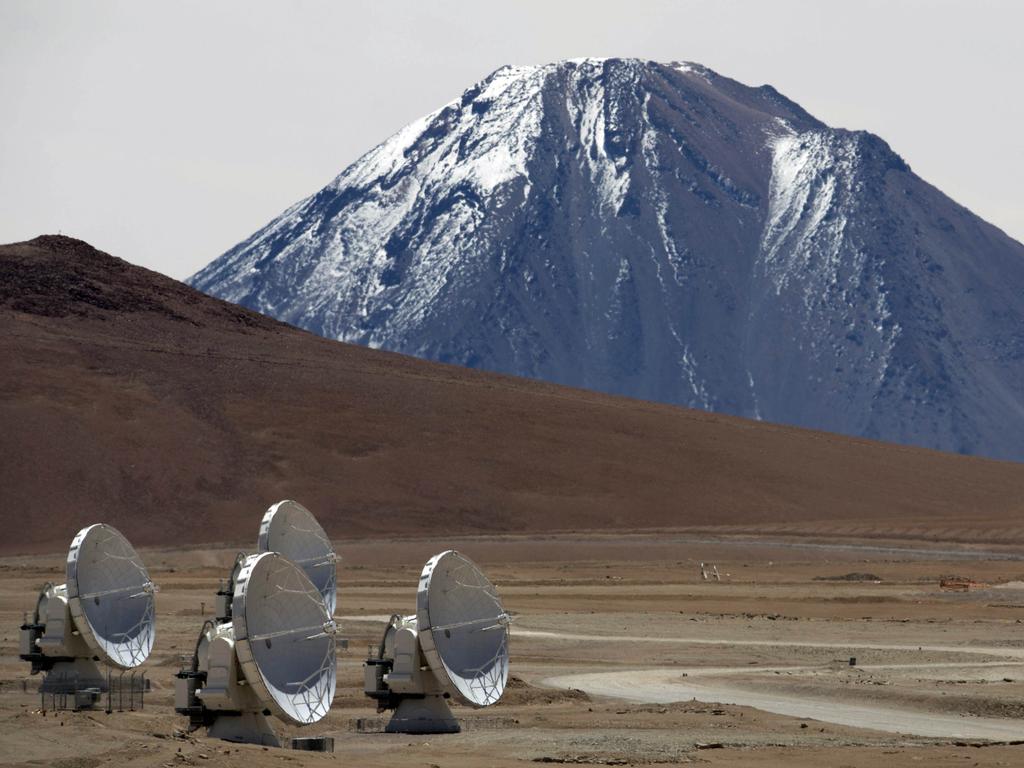

These later observations and computer modelling* have determined that the quasar is gobbling up the equivalent of 370 suns a year — roughly one a day. Further analysis showed the mass of the black hole to be 17 to 19 billion times that of our sun, according to the team. More observations are needed to understand its growth rate.
The quasar is 12 billion light-years away and has been around since the early days of the universe. A light-year is 9.46 trillion km.
WATCH THE VIDEO

POLL
GLOSSARY
- astronomers: scientists who study the stars, planets and other natural objects in space
- quasi-stellar: class of huge, very bright objects beyond our Milky Way that look starlike
- emitter: something that sends out a light, noise or substance
- equivalent: comparable, equal, similar, the same as or has the same effect as something else
- immense: huge, enormous, massive
- ferocious: fierce, savage, violent
- luminous: shining or glowing with light, very bright
- cosmic: relating to the universe or outer space
- galaxy: a huge collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars and their solar systems, all held together by gravity
- telescope: a tool that astronomers use to see faraway objects
- Atacama Desert: considered one of the driest coastal deserts in the world, located along the west (Pacific) coast of South America, mainly in northern Chile
- misclassified: put in the wrong category, mistakenly classified
- computer modelling: using a computer to make a model of a plan or design
EXTRA READING
Astronomers discover ‘biggest ever’ black hole
Black hole eats an Earth every second
QUICK QUIZ
- What is the word “quasar” short for and what does it mean?
- The quasar shines how many times greater than our sun?
- How many times larger than our sun is this record-breaking quasar?
- It was incorrectly classified until last year as what?
- Observations and computer modelling have determined the quasar is doing what?
LISTEN TO THIS STORY
CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES
1. Cosmic hurricane?
What would a cosmic hurricane look, feel and sound like? Write a story, create an artwork or make something inspired by this question.
Time: allow at least 30 minutes to complete this activity
Curriculum Links: English, Science, Visual Arts
2. Extension
What is the most interesting, amazing or strange fact or part of this story for you? Write paragraphs explaining your choice and what you would love to find out more about it.
Time: allow at least 20 minutes to complete this activity
Curriculum Links: English, Science
VCOP ACTIVITY
Looking across the universe
How amazing is space?!
The description of the quasar and its black hole really creates a vivid image in our minds.
Imagine that you have been given the opportunity to look through the astronomers’ telescopes deep into the universe. Describe in detail what captures your eye. Maybe it’s something you witnessed recently, like the red moon, but up close.
Use your VCOP skills to create a clear image for the audience.

