How Greek Mythology continues to have a large influence on our modern lives
From the Olympic Games to the star signs we are born under and the brands we wear when we play sport, Greek Mythology continues to have a huge impact on our modern lives

READING LEVEL: GREEN
It is more than 2000 years since the time of the Ancient Greeks, but Greek Mythology continues to have an influence on how we live today in western society.
References to Greek Mythology can still be found in our discussions about science, arts and literature, language, names and brands.
Thinkers from Ancient Greece also laid the foundations for many areas of study including astrology, mathematics, biology, engineering, medicine or linguistics*.
Everywhere you turn, there is likely to be a reference to Greek Mythology. In the brand of the sports shoes you are wearing, the name given to your breakfast meal, the way a building has been constructed, the music you are listening to or the poem you are studying at school.
Here are some common links in key areas:

NAMES
- Amazon: The online retail store is named after the group of strong women warriors who were trained in combat and archery and known as the Amazons.
- Pandora: The jewellery brand took its name from the first mortal woman in Greek mythology, her name meant all-gifted.
- Hermès: He was the messenger of the Greek Gods, but today you will see this name for the company that specialises in luxury goods, lifestyle accessories and perfumes.
- Dove: The dove was a symbol of Aphrodite, the Goddess of beauty. Unilever owns a personal care brand by the same name.
- Apollo: The US Apollo Space Program to take astronauts to the moon was named after Apollo, based the God’s ability as an archer to hit his target.
- Nike: The US sports apparel company is named after the Greek Goddess of victory.
- Cerberus: The Australian Royal Navy has a training facility in Victoria named HMAS Cerberus, after the multi-headed dog that guarded the gates of the Underworld.
- Cereal: the generic name for our breakfast meal is named after Ceres, the God of grain.
Even the names of baby boys and girls are still drawn from Greek Mythology.
Some well-known mythical names used today include:
Boys
- Jason: from the Greek hero Jason who led the Argonauts.
- Troy: from the Greek city of Troy.
- Damon: was a loyal friend of Pythias in Greek Mythology.
Girls
- Helen: from Helen of Troy, who was the daughter of Zeus.
- Rhea: the name of Zeus’s mother.
- Penelope: in The Odyssey, Penelope is the wife of Odysseus.
- Phoebe: was a Titan associated with the moon.
BRANDS
Several major car companies have borrowed names from Greek Mythology for their vehicles. These include:
- Buick Apollo
- Volkswagen Eos
- Honda Odyssey
- Nissan Titan
- Ford Taurus
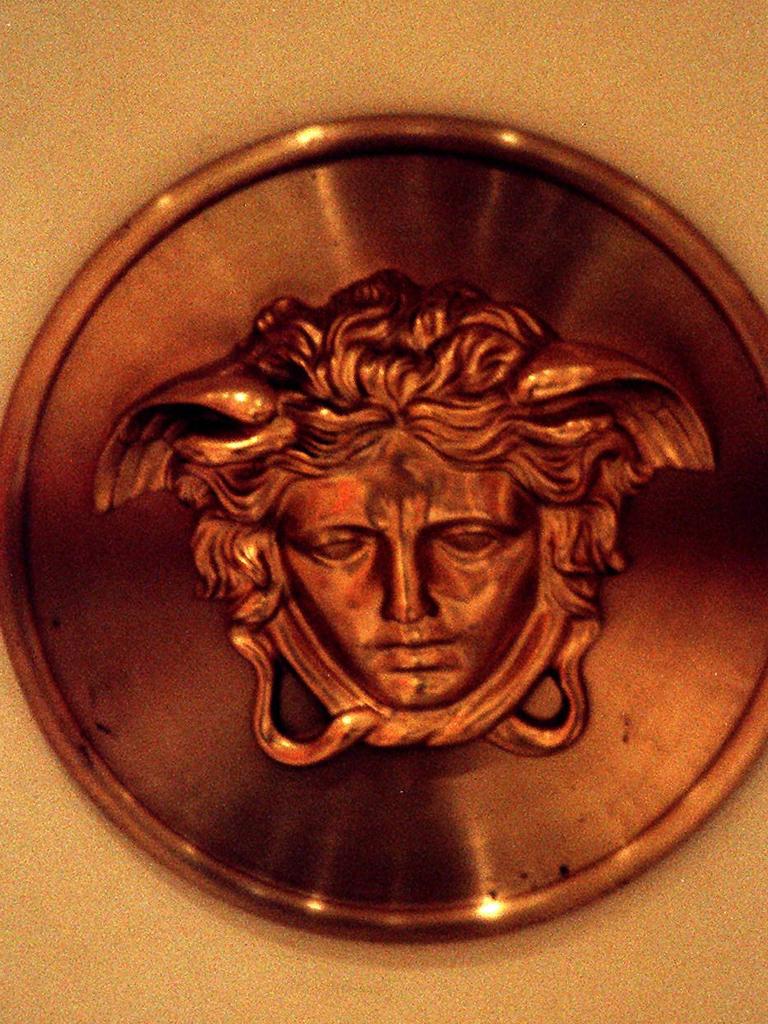


LOGOS
- Medicine: the medical profession is symbolised by the snake-entwined staff* of the God of Medicine, Asclepius.
- Versace: the fashion house has Medusa as its logo after founder Gianna Versace likened his clothing to the mythical creature in that it had “fatal attraction”.
THE MODERN OLYMPICS
The Olympic Games started in Ancient Greece in the city of Olympia. The participants were the city-states of Ancient Greece and its colonies.
The Olympic Games were held every four years in honour of Zeus, the King of the Gods.
The prizes for winning were fame and glory. Statues of the winners were built and sometimes the winners’ faces were even put on coins.
The Olympics of Ancient Greece lasted from the 8th century BCE to the 4th century BCE before dying out.
Inspired by the ancient Olympics, Baron Pierre de Coubertin revived the event by founding the International Olympic Committee (IOC) on June 23, 1894, and the modern Olympic Games were born.
Today we still celebrate some of the old traditions, such as the olive leaf crowns on winners’ heads, the lighting of the Olympic flame, and the Opening and Closing celebrations.
The first Games put on by the IOC were held in Athens during the summer of 1896. The 1896 Summer Olympics brought together 14 nations and 241 athletes who competed in 43 events.
SPORTING TEAMS
Across the world there are plenty of clubs and teams named after characters from Greek Mythology.
In Australia we have the Gold Coast Titans in the NRL. In the US, college and school football and basketball teams are regularly named after the Titans, Trojans and Spartans.
In America’s National Football League, the Orlando Apollos drew inspiration for their name from the God Apollo.
And, as you would expect, many Greek football clubs have names with links to their own mythology.
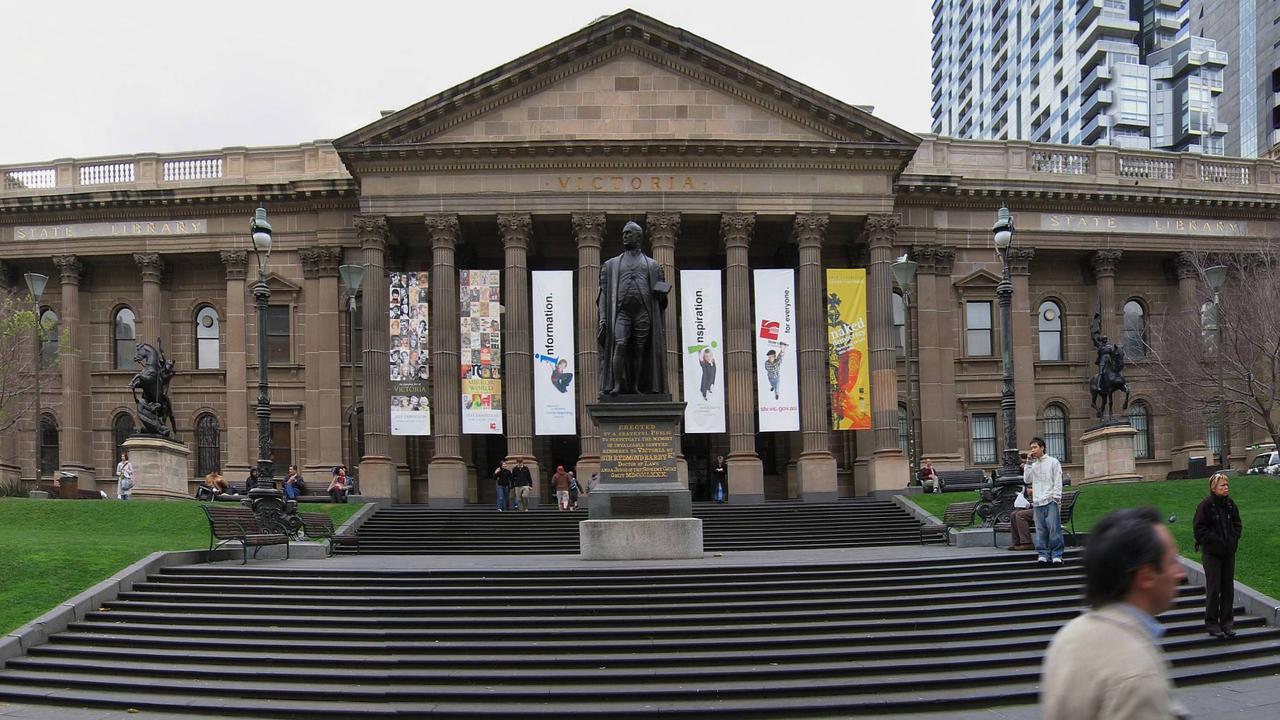

BUILDINGS
The columns or pillars you see on grand buildings today are most likely inspired by Greek architecture.
The most famous example of Greek architecture is the Parthenon, a magnificent building with pillars located in Athens. It was a temple dedicated to Athena, Queen of the Gods, from the people of Athens.
Each Greek structure was inspired by the story and unique abilities of a specific God.
Today, pillars are used in many public buildings such as churches and libraries. One famous modern-day building is the White House in America where President Donald Trump lives.
Each aspect and characteristic of Greek architecture was designed to complement and relate to one another.
There are three systems of architecture, known as orders — the Doric, the Ionic and the Corinthian.
Some Australian buildings inspired by Greek architecture include:
- State Library of Victoria in Melbourne
- Darlinghurst Courthouse, Sydney
- St George’s Church, Battery Point, Hobart
POP CULTURE AND THE ARTS
Greek mythology has been used in nearly every form of popular culture. Many Greek myths have been adapted into modern novels, movies, TV shows and video games.
The word “theatre” is derived from the Greek word “theatron”, meaning the seating section of outdoor arenas where people watched plays. The first western theatre originated in Athens, and was, like many other Ancient Greek theatres, a semicircular structure cut into a hillside that was capable of seating 10,000 to 20,000 people.
Some well-known instances of Greek mythology in pop culture are:
- Disney’s Hercules cartoon movie
- The best-selling novel Percy Jackson and the Olympians
- The TV show Battlestar Galactica
- Mary Shelley’s Gothic novel Frankenstein
VIDEO: Official trailer for the recent movie Hercules, starring Dwayne “the Rock” Johnson.

The earliest visual representations of mythological characters and symbols occurred in late Mycenaean* and sub-Mycenaean art with Centaurs, a Siren, and even Zeus’s lover Europa being recognised.
Mythological and epic themes are also found in Geometric art of the 8th century BCE, but not until the 7th century did such themes become popular in both ceramic vases and pots and sculptured works.
In later periods, they became commonplace.
Artwork showing the birth of Athena appears on the east pediment* of the Parthenon in Athens, and the legend of Pelops and the labours of Heracles are on the corresponding pediment.
The battles of gods with giants and of Lapiths (a wild race in northern Greece) with Centaurs were also favourite motifs.
Greek myths influenced poets such as Dante and Petrarch in Italy and Geoffrey Chaucer in England and, later, the English Elizabethans and John Milton.
Jean Racine in France and Johann Wolfgang von Goethe in Germany revived Greek drama, and nearly all the major English poets from William Shakespeare to Robert Bridges turned to Greek Mythology for inspiration.
The German composers Christoph Gluck (18th century) and Richard Strauss (20th century), the German-French composer Jacques Offenbach (19th century), the Russian composer Igor Stravinsky (20th century), and many others have set Greek mythological themes to music.
The Greek myths have also been the inspiration for a number of operas.

ASTRONOMY
The names of the Zodiac, which is your star sign from your birth date, all have their beginnings from Greek Mythology.
- Aquarius, the Water Bearer: comes from a Greek myth about a flood after Zeus poured all the waters from the heavens out onto the Earth to wash away and destroy the wicked and evil men.
- Aries, the Ram: Zeus placed a golden ram’s image among the stars in honour of its heroism.
- Cancer, the Crab: was a creature sent by the Goddess Hera to destroy Heracles.
- Capricorn, the Goat: in Greek Mythology, Capricorn is the God Pan, who was half man but goat from the waist down and had goat’s horns for ears.
- Gemini, the Twins: the twins were Castor and Polydeuces (Pollux). Together, they were known as the Dioscuri.
- Leo, the Lion: linked to the Labours of Heracles and his first task, which was to kill the Nemean Lion.
- Libra, the Scales: represent balance and justice, harmony and equilibrium. In Greek Mythology, the Goddess of Justice is Themis and she is pictured holding the scales.
- Pisces, the Fish: named after Aphrodite and Eros who were turned into fish by Zeus to help them escape danger.
- Sagittarius, the Centaur: named after the Centaur Chiron, who taught men medicine and was kind to Jason of the Argonauts.
- Scorpio, the Scorpion: was the creature created to sting and kill the hunter Orion.
- Taurus, the Bull: named after the white bull Zeus turned himself into to help win the affections of Europa.
- Virgo, the Maiden: named after the Goddess of Innocence and Purity, Astraea.
GLOSSARY
- linguistics: study of language and its structure
- staff: a long stick
- Mycenaean: relating to a late Bronze Age civilisation in Ancient Greece
- pediment: the triangular upper part of the front of a classical building
EXTRA READING
Part Six: Villains and tales with a twist
Part Seven: Monsters, animals and beautiful Sirens
QUICK QUIZ
- Name three brands that draw their names from Greek Mythology.
- Fashion house Versace uses which Greek character in its logo?
- Who revived the Olympic Games?
- Which famous building in America has Greek architecture?
- The star sign Leo honours which mythical creature?
LISTEN TO THIS STORY
CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES
Refer to the accompanying FREEE Greek Myths and Legends classroom workbook with 25 activities at https://kidsnews.myshopify.com/products/greek-myths-and-legends.

